Participation and action
Have a listen to the young people in the videos below.
Robbie Strathdee has recently left Horsforth High School in Leeds, where he worked as a student to help make the school a greener place. Robbie became involved in the Youth Strike for Climate movement very soon after it started in 2019 and is a key organiser and spokesperson for the Leeds Youth Strike. He has been involved in making representations to Leeds City Council about how the Council could take youth voices into account in implementing their Climate Emergency plan.
Now read the read the Feelings and Behaviour section from the Big ideas on Climate Action.

Have a look at Hart’s theory on the different levels of youth participation.
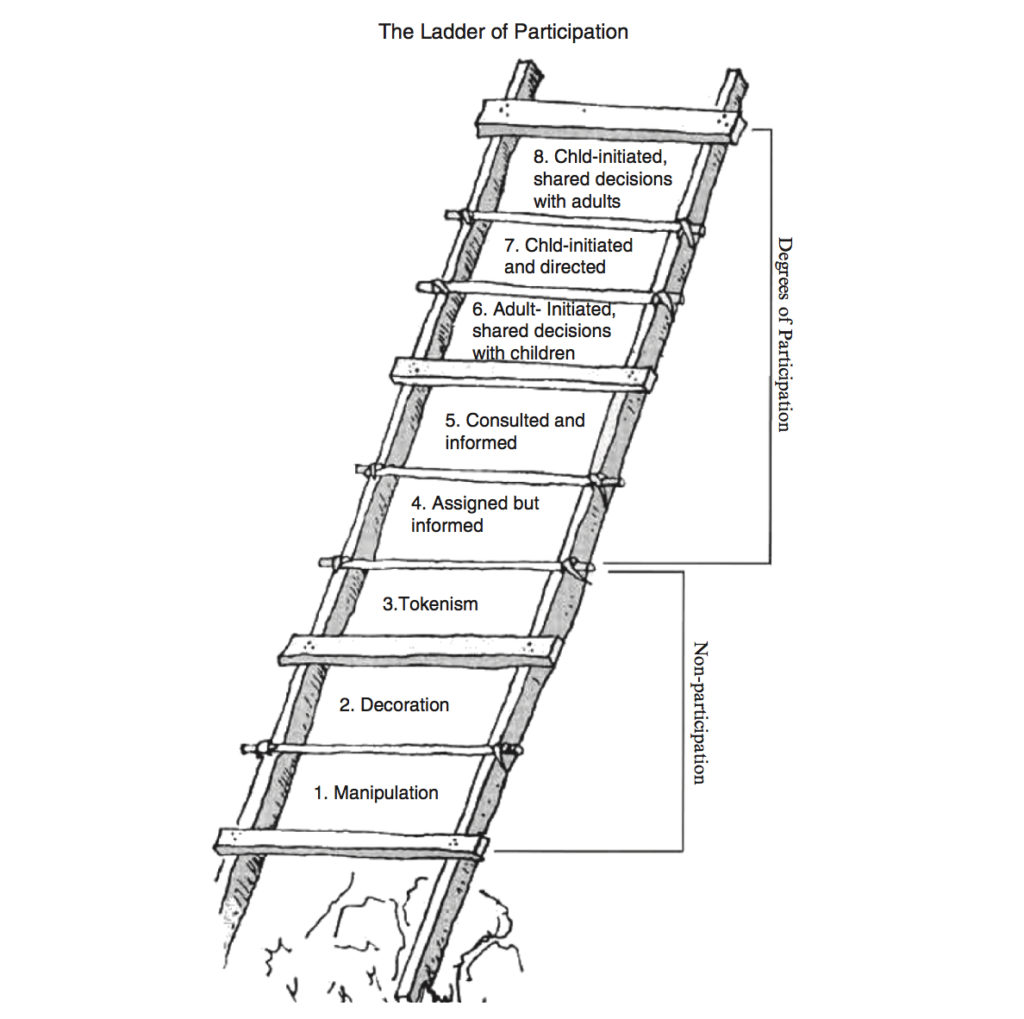
The Ladder of Children’s Participation
Hart’s typology of children’s participation is presented as a metaphorical “ladder,” with each ascending rung representing increasing levels of child agency, control, or power. In addition to the eight “rungs” of the ladder represent a continuum of power that ascends from nonparticipation (no agency) to degrees of participation (increasing levels of agency). It should be noted that Hart’s use of the term “children” encompasses all legal minors from preschool-age children to adolescents.
The eight rungs of Hart’s Ladder of Children’s Participation are:
1. Manipulation
RUNG 1 – Manipulation: Adult-led activities, in which youth do as directed without understanding of the purpose for the activities.
2. Decoration
RUNG 2 – Decoration: Adult-led activities, in which youth understand purpose, but have no input in how they are planned.
3. Tokenism
RUNG 3 – Tokenism: Adult-led activities, in which youth may be consulted with minimal opportunities for feedback.
4. Assigned but Informed
RUNG 4 – Assigned, but informed: Adult-led activities, in which youth understand purpose, decision-making process, and have a role.
5. Consulted and Informed
RUNG 5 – Consulted and informed: Adult-led activities, in which youth are consulted and informed about how their input will be used and the outcomes of adult decisions.
6. Adult-Initiated, Shared Decisions with Children
RUNG 6 – Adult initiated shared decisions with youth: Adult-led activities, in which decision making is shared with youth.
7. Child-Initiated and Directed
RUNG 7 – Youth initiated and directed: Youth-led activities with little input from adults.
8. Child-Initiated, Shared Decisions with Adults
RUNG 8 – Youth initiated shared decisions with adults: Youth-led activities, in which decision making is shared between youth and adults working as equal partners.
Use Hart’s theory to complete the tasks below.